Maine
Rank
Maine, ranked 27th with a C-, sees innovation budding cautiously. Parent-led efforts and district initiatives show promise, but a limited charter landscape keeps options frustratingly narrow in the Pine Tree State.
The beauty of Maine notwithstanding, the environment for charters here is hardly green. Maine has the seventh weakest state in the nation.
Career and Technical education is a major focus in Maine, empowering middle and high school students to participate in programming at one of the state’s 27 CTE centers, and even graduate with a CTE diploma. While Innovation Public Zones are allowed, the...
Governor Mills, the daughter of a public-school teacher and someone who raised five daughters who attended public schools, has yet to publicly acknowledge the power of school choice. Her leadership impartiality is mirrored in the state legislature. It may be...
The second oldest program in the country, dating back to 1873, made its Supreme Court debut in 2022! While the program has always permitted students who do not have public schools in their towns to take their money to non-sectarian schools of choice, some...
More than a dozen states made major gains in education freedom this year by passing or expanding ESA programs, signaling a powerful shift toward student-centered funding.
While not clearly accessible using the dropdowns on Maine’s Department of Education homepage, school report cards can be found using the search bar or by accessing the “ESSA Dashboard” section. Measures like student demographics, per-pupil spending, teacher...

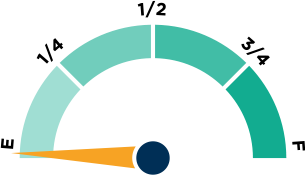
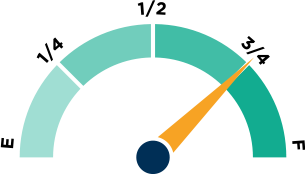
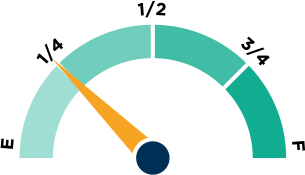
One of many data points to assess whether a state has the right policies in place to ensure teacher quality is the "use of student achievement data in teacher preparation accountability." How empty or full the fuel tank above is will give you the answer for your state.
Blaine is dead and opportunity is consequently growing in the Pine Tree state. In December 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court argued in Carson v. Makin and in a 6-3 ruling, that a state may not prohibit families that participate in educational choice programs from...